Free shipping – how to use it to increase online shop’s earnings?
- 06 July 2021
Customers are more and more used to free shipping. The reason is the popularity of such programs as Amazon Prime or Walmart+. Some of the online shops implement it as well – to attract more customers but also to increase the average order value (AOV). Is it worth it for an online shop to offer free delivery? How to manage pricing when offering free shipping? What are different approaches to “free shipping”?
Free delivery – why has it become so popular?
The popularity of free shipping can be surprising – after all, it is an additional cost that the enterprise decides to cover instead of transferring it on to the customers. Why does an online store do that?
First of all, free shipping can be used to increase the AOV – average order value. Online stores expect to sell more to customers when they try to reach the threshold that qualifies them for free delivery. We describe it further later in the article.
The second reason is an intuitive one: online shops believe that free shipping will make a decisive difference that will convince the consumer to purchase at their store. Or, in the case of more competitive markets – retailers don’t want to frighten the potential customers by the lack of free shipping. If you look at price comparison websites or marketplaces, the popularity of free delivery makes offers that don’t offer it stand out. As an example, just have a look at the listing on Google Shopping. Information about free shipping is one of the first ones that a customer can see when he compares different offers (information on delivery is in the second column):
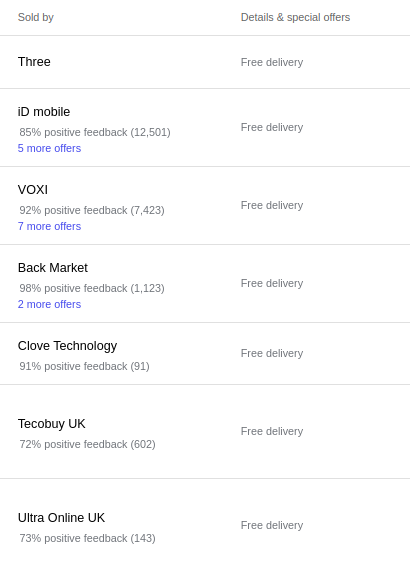
Free shipping as a competitive advantage
The competition on such platforms as Google Shopping, Idealo or Amazon is significant. Based on an analysis of more than 18 thousand offers for 553 electronics products, the average number of offers per product on Google Shopping UK is 18.6, whilst on Amazon and Idealo – both 7.4. You can check details here: Where to check prices of electronics products? Amazon, Google Shopping and Idealo analysis.
Having such a choice, customers can easily filter out these offers that don’t offer free shipping:
How important is free shipping for customers’ purchasing decisions and what is its influence on a company’s sales? The research shows that it can have a significant impact:
- Cost of shipping is the most popular reason for shopping cart abandonment (86%) according to FuturePay.
- 93% of shoppers claim they will take action to qualify for free shipping by adding items to their cart (according to Shippo).
- 40% of shoppers would buy more if they were offered free shipping (Deloitte).
Based on that, you can see that free shipping can be helpful in customer acquisition and increasing order value. Does it need to always look the same though?
Different approaches to free shipping
“Free delivery” doesn’t always mean that a client doesn’t need to pay anything for shipping regardless of the purchased goods. One can easily imagine situations where such an approach would be unprofitable for the company. As an example – when the product value is lower than the value of shipping. What are the most popular approaches to free shipping then?
Setting a free shipping threshold
It is one of the most popular approaches. Customers get free shipping under the condition that the purchase is higher than e.g. $100.
How to choose the proper threshold?
First, you should calculate the average product margin. Based on that, you can determine what order value generates on average the sufficient profit value after deducting the shipping cost.
Secondly, you should look at the current average order value. Setting the threshold over this value can motivate clients to increase their order value and hence increase sales. After all, most of them prefer to spend more and get a tangible product rather than pay for the delivery.
And thirdly – don’t forget about the power of tests. Change the threshold and check what is the impact on your profits. Does lowering the threshold lead to higher sales? Does increasing the price entail higher AOV? Test to find the ideal value.
Unconditional free shipping
No matter the purchase, the shipping is free. It is a highly risky approach, especially if the shop has low-margin products in the offer. The profit earned on the sale can be lower than the cost of shipping.
Free shipping for members / registered users
Instead of money, you can charge customers in different ways – by incentivizing them to share with you contact data. Free shipping only for newsletter subscribers can motivate the subscription. An example of a programme with exceptionally good shipping options is of course Amazon Prime. The members get unlimited free two-day shipping on eligible items, with no minimum spend.
Free shipping under the condition of specific products purchase
The online shop can offer free shipping only under the condition that some products are in the shopping cart. There are two approaches – the requisite product can be the key product in the retailer’s portfolio or, contrary – a product that doesn’t sell well and lags in the warehouse.
Free shipping as a promotion
Free shipping can be a form of a temporary promotion and used in marketing announcements. Beware of making free shipping a constant “promotion” – don’t say it is exceptional if, in reality, you offer it all the time. However, if you implement it only on special occasions (e.g. Black Friday), highlight the time limits to use the FOMO mechanism (fear of missing out). You can read more in our article about psychological pricing.
Click and collect
This approach is situated somehow “in the middle”. The customer doesn’t need to pay for the delivery but he needs to make the effort to go to the physical shop or a pickup point to get the order. Additionally, such an option is available only for those customers that live in specific locations. However, click and collect turned out to be quite a popular solution for supporting local retailers during the pandemic – you can read more about this phenomenon in the interview with Karsten Holdorf.
Price management and free shipping
Offering free shipping has an obvious influence on pricing. The cost of shipping tends to be calculated into the product price to compensate for this cost.
However, we recommend starting with the competitive position analysis in the situation when the shipping is included and when it is not. Why?
On price comparison websites, customers usually can choose between sorting offers by price including delivery charges or without them. Just have a look at the screenshot from Idealo:
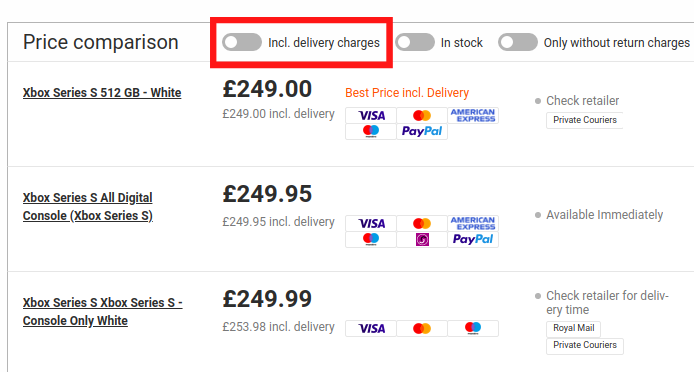
If you use a competitor price monitoring, you probably are always aware of how competitive your shop’s offer is. But do you look at prices that include the shipping cost or not?
In the Dealavo app, you can easily switch the views – the one in which the delivery cost is included and the one where it is not. You can find this option in the advanced filters section:
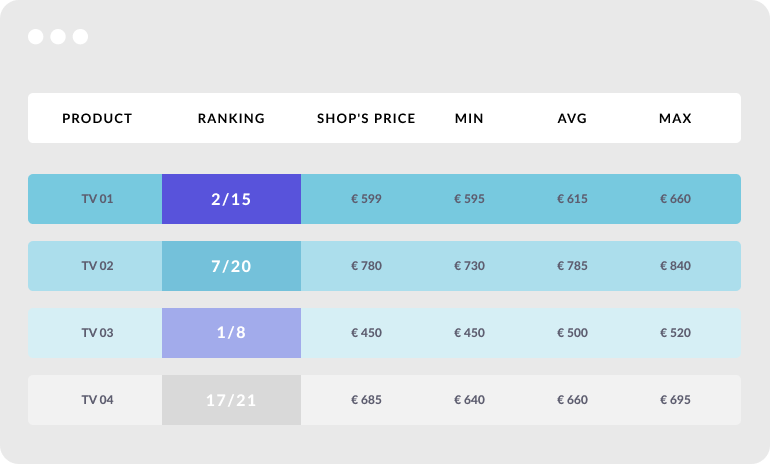
Based on that, the shop can easily check which place in the ranking (listings) it takes and how attractive it is depending on the way customers sort the offers:
You can read more in our article: What is a price tracking tool and how to choose the best one?
Free shipping on Amazon vs. pricing
Free shipping on Amazon is available not only for Amazon Prime members – the “regular” customers can get the free shipping if their order value is higher than $25 (in the past, it used to be $49). It is eligible for products offered by sellers operating in the FBA model.
What does it mean for retailers? If you sell a product that costs approximately $25 it probably makes sense not to lower the price below $25 (e.g. $24.99). One cent doesn’t make a big difference to customers, but the lack of free delivery does.
One could argue that it motivates customers to add additional items to the basket but the truth is that Amazon is different from the shop’s website. On the marketplace, customers can easily choose another offer that is a few cents more expensive and take advantage of the free shipping.
How to include this aspect if you use dynamic pricing in your pricing strategy? You can easily set customized pricing rules with a lower limit – that the price shouldn’t be lower than $25. Thanks to that, your pricing will quickly adjust to the market situation without the risk of losing competitiveness because of the lack of a free shipping option.
Offering free shipping – is it worth it?
Is it worth offering free shipping after all?
A cheap and fast delivery is something more and more customers are used to – especially due to such programs as Amazon Prime or Walmart+. In some industries, such as e-grocery, it is one of the key elements – we have described it further in our article: Online grocery shopping – a trend that is here to stay.
However, offering unconditional free shipping usually is too risky for online shops and can lead to a profit decrease. That is why every retailer should start by calculating the average profit margin, average order value and analyzing competitive position to make sure the delivery options he provides entail higher, and not lower, profits.